Pydon Software Reference
After you have installed Pydon, you can use Pydon to interface with your Sense/Stage network using Open Sound Control (OSC) messages.
There are two options for using Pydon, through a GUI interface, or through a command-line script.
GUI version
The GUI can be started in the following ways:
- On Linux and OSX from the command line with
pydongui.py - On Windows by double clicking on the file
start_pydon.bat
A window will open that looks something like this:
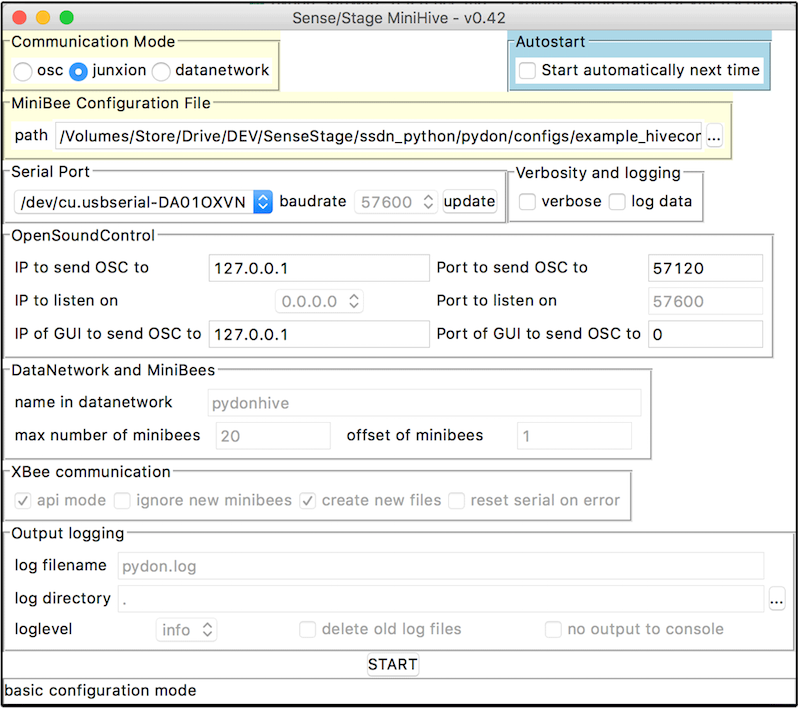
The window offers you a number of settings that can be adjusted before you actually start your Sense/Stage network. Some of the most important settings you should know about are:
- Communication mode: this defines the format of OSC messages that will be used to communicate with your sensor network. Which one you choose largely depends on the type of messages that are easiest to work with in the program that will be receiving data from your network. The Choices are:
- osc – This is one option for communicating with your network using simple OSC messages. Incoming data from your network is sent using the message ‘‘/minibee/data’’ where the first data element is the unique id number of the minibee, followed by its sensor values.
- junxion – Uses a slightly modified version of the ‘osc’ option above. Incoming data from your network is sent such that the id number of the minibee is part of the message address, for example, if your minibee id was 2, you would receive the sensor data from this minibee via the message ‘‘/minibee/data/2’’.
- datanetwork – Uses the SenseWorld DataNetwork to transfer the data to multiple clients using the DataNetwork framework. If you don’t know what this is, then don’t use it.
As you switch between the different communication options, settings that are relevant to these options will become enabled.
-
MiniBee configuration file: this is an XML file containing information on what kind of sensors are attached to your minibees. Examples are provided in the download of the pydon package. For documentation on the format, read this page. You can browse to the appropriate configuration file using the […] button.
-
Serial port: here you need to select the serial port to use. The dropdown menu provides all ports that are found on your computer.
-
OSC communication: here you can define the target host and port to send OSC data to. For most cases this will be your local host with a port that is specified in your client software.
-
Verbosity: these options provide more detailed output messages as the program is running; they are mainly meant for debugging, or recording data in a raw format. In a final production you would leave these options off.
- Autostart: this is an option to automatically start with the last used settings the next time the program is started. This allows for a somewhat quicker start-up time once your project settings have been finalized.
In the [Options] menu, you can select the [Advanced] mode, which will allow tweaking advanced settings. The settings are described in detail here. In most cases you will not need to use the advanced settings.
By clicking [START] you start the communication between your computer and the Sense/Stage network, you will also begin to receive OSC messages. At this point your current settings are stored to a file named pydondefaults.ini in the directory from which you start pydongui.py. The next time you start pydongui.py it will read the settings from this file and use these as defaults. The program will look for the last used settings in the directory from which you start pydongui.py.
Command line interface
Alternatively you can use the command line interface:
$ pydoncli.py
Options are taken from the file pydondefaults.ini that should be in the same folder as from where you call the script. If no pydondefaults.ini file is chosen, sensible default values are used instead.
If you provide additional command line parameters, these will take precedence over the parameters defined as default and stored as the new defaults in pydondefaults.ini.
To see which parameters are available you can type:
$ pydoncli.py -h
To start it you would do for example:
$ pydoncli.py -P osc -c configs/example_hiveconfig.xml -s /dev/ttyUSB0
/dev/ttyUSB0 is the address of your serial port, on a Mac it will be something like: /dev/tty-usb.serialASSFADF0002332:
$ pydoncli.py -P osc -c configs/example_hiveconfig.xml -s /dev/tty-usb.serialASSFADF0002332
If you want to send the data to another machine:
$ pydoncli.py -c nameofconfigfile.xml -d 192.168.0.7
where 192.168.0.7 is the IP address of the other machine.
If you need to figure out what is going on, there is a verbosity switch, which will print more output:
$ pydoncli.py -c example_hiveconfig.xml -s /dev/ttyUSB0 -v True
Available parameters on the command line interface
Output of $ pydoncli.py -h:
Usage: pydoncli.py [options]
MetaPydonHive - Create a client to communicate with the minibee network.
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-P PROGRAM, --program=PROGRAM
Which program/infrastructure do you want to use?
options: datanetwork, osc, libmapper, junxion
-s SERIAL, --serial=SERIAL
the serial port [default:/dev/ttyUSB0]
-a APIMODE, --apimode=APIMODE
use API mode for communication with the minibees
[default:False]
-v VERBOSE, --verbose=VERBOSE
verbose printing [default:False]
-u IGNORE, --ignore-unknown=IGNORE
ignore unknown minibees [default:False]
-f CREATENEWFILES, --create-new-files=CREATENEWFILES
create new files for unknown minibees [default:True]
-x XBEEERROR, --check-for-xbee-error=XBEEERROR
check whether xbee-error occurred [default:False]
--auto=AUTOSTART autostart [default:False]
-l LOGDATA, --logdata=LOGDATA
log data to file [default:False]
-c CONFIG, --config=CONFIG
the name of the configuration file for the minibees
[default:../configs/example_hiveconfig.xml]
-n NAME, --name=NAME the name of the client in the datanetwork
[default:pydonhive] (needed for datanetwork or
libmapper)
-b BAUDRATE, --baudrate=BAUDRATE
the serial port [default:57600]
-m MINIBEES, --nr_of_minibees=MINIBEES
the number of minibees in the network [default:20]
-o MBOFFSET, --minibee_offset=MBOFFSET
the offset of the number range for the minibees in the
network [default:1]
-d HOST, --host_ip=HOST
the ip address of the datanetwork host or osc/junxion
receiver [default:127.0.0.1]
-t HPORT, --host_port=HPORT
the port on which the application that has to receive
the OSC messages will listen [default:57120] (needed
for osc or junxion or default for datanetwork)
-i IP, --ip=IP the ip on which the client will listen
[default:0.0.0.0]
-p PORT, --port=PORT the port on which the client will listen
[default:57600]
-N LOGNAME, --logname=LOGNAME
log name (default pydon.log)
-V LOGLEVEL, --loglevel=LOGLEVEL
logging level (debug, info, error)
-L LOGDIR, --logdir=LOGDIR
log DIRECTORY (default ./)
-Q, --quiet do not log to console
-C, --clean remove old log file
| page created on: | last changed on: |
|---|---|
| 6 February 2017 | 4 September 2019 |
